Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Of Aldehydes And Ketones Pdf
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Of Aldehydes And Ketones Pdf. Addition of hydrogen cyanide to aldehydes and ketones. Several nucleophiles such as water, alcohols, cyanide etc attack the carbonyl carbon.

 Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition from documents.pub
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition from documents.pubHowever, the majority of characteristics reactions of aldehydes and ketones involve a nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl group. Therefore, nucleophilic addition reactions occur for carbonyl and formyl groups. Some addition reactions are given below :

However, the majority of characteristics reactions of aldehydes and ketones involve a nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl group. A condensation reaction is one in which two molecules join together with the loss of a small molecule in the process.

The nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl group is the most important reaction of aldehydes and ketones. Facts and a simplified mechanism for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones using sodium tetrahydridoborate, nabh 4.

The initial nucleophilic addition step occurs by the usual mechanism and yields an. The reaction can be catalyzed.

Addition of hydrogen cyanide to aldehydes and ketones. The nucleophilic addition reaction between hydrogen cyanide (hcn) and carbonyl compounds (generally aldehydes and ketones) results in the formation of cyanohydrins.

¥the addition reaction is reversible. We defer our more detailed discussion of nucleophilic addition reactions to later chapters.
Addition reactions to carbonyl compounds note: These hydrogens are referred to as α hydrogens, and the carbon to which they are bonded is.

The initial nucleophilic addition step occurs by the usual mechanism and yields an. The many reactions involving aldehydes and ketones are sufficient for different synthesis reactions.

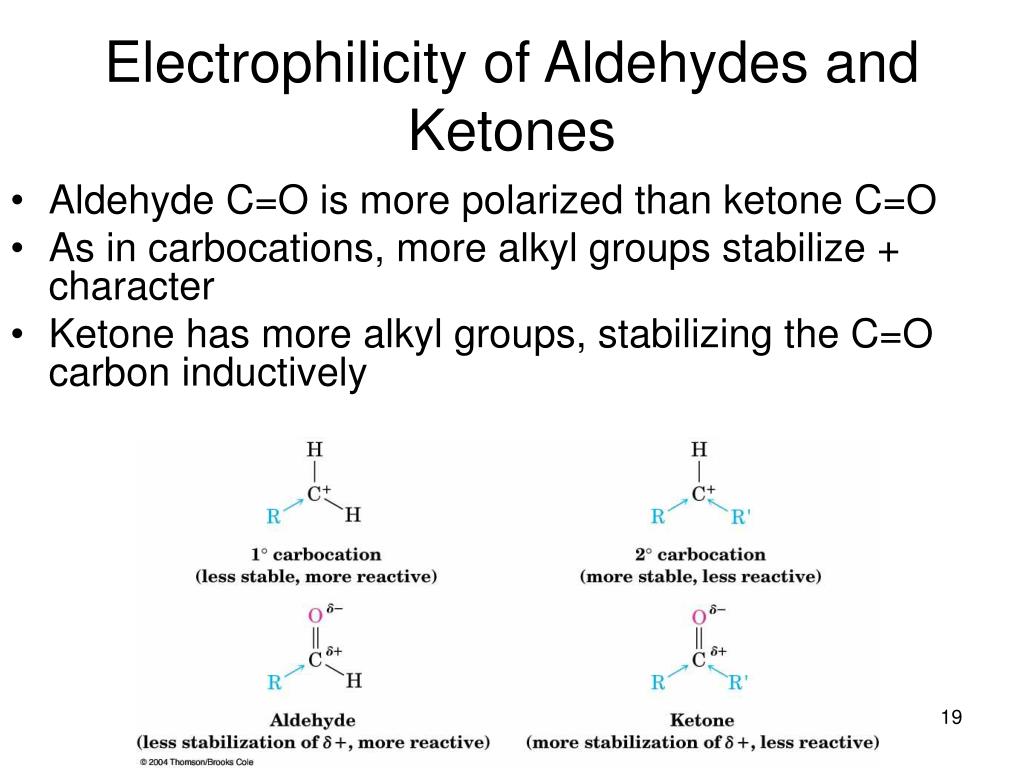
Explain why, in general, aldehydes under nucleophilic addition reactions more easily than ketones. As the nucleophile attacks the carbonyl group, the carbon atom changes from sp2 to sp3.
Nucleophilic addition reactions are common in aldehydes and ketones as we already discussed in properties of aldehydes and ketones. The many reactions involving aldehydes and ketones are sufficient for different synthesis reactions.

Nucleophilic addition reactions | find, read and cite all the research you need on researchgate The addition of hydrogen cyanide to aldehydes and ketones.

As the nucleophile attacks the carbonyl group, the carbon atom changes from sp2 to sp3. The reaction can be catalyzed.
The reaction is known as a condensation reaction. 908 chapter 19 • the chemistry of aldehydes and ketones.

In this case, that small molecule is water. Ch18 ketones and aldehydes (landscape) page 15 reactions of aldehydes and ketones the most common reaction of aldehydes and ketones is nucleophilic addition.

The reaction can be catalyzed. In the case of ketones, there are alkyl chains next to the c=o carbon atom.
Aldehydes and ketones react with hydrogen cyanides to give cyanohydrin. But, it should be noted that all adducts of this addition reaction are not stable and many reaction are readily reversible.

We defer our more detailed discussion of nucleophilic addition reactions to later chapters. When it attacks on one side, it will produce one enantiomer and when it attacks on the other side, it will produce the other enantiomer

The reduction of aldehydes and ketones. This is the case when aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition with hydrogen cyanide, hcn;

In this case, that small molecule is water. ¥the addition reaction is reversible.

As the nucleophile attacks the carbonyl group, the carbon atom changes from sp2 to sp3. The mechanism of imine formation begins as a nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl group.

The mechanism of imine formation begins as a nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl group. The nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl group is the most important reaction of aldehydes and ketones.
However, The Rate Of Reaction Can Be Increased By Using Acid Or Base.Carbon is sp 2 hybridized. These hydrogens are referred to as α hydrogens, and the carbon to which they are bonded is. As water is a relatively poor nucleophile the rate of addition is slow.
The Initial Nucleophilic Addition Step Occurs By The Usual Mechanism And Yields An.Addition of hydrogen cyanide to aldehydes and ketones. There are two ways of increasing the rate of reaction in a nucleophilic R, r'(h) all lie on the same plane and are 120 0 apart.
Explain Why, In General, Aldehydes Under Nucleophilic Addition Reactions More Easily Than Ketones.Because the net result is the addition of a molecule of The reduction of aldehydes and ketones. Keywords make sure you can define and use the keyword below in context.nucleophilic addition reaction study notes we have already discussed electrophilic
Therefore, Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Occur For Carbonyl And Formyl Groups.Facts and a simplified mechanism for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones using sodium tetrahydridoborate, nabh 4. 908 chapter 19 • the chemistry of aldehydes and ketones. The reaction of ethanal with hcn is given below.
¥The Addition Reaction Is Reversible.An aldehyde or ketone to form the corresponding hydrate. We defer our more detailed discussion of nucleophilic addition reactions to later chapters. A condensation reaction is one in which two molecules join together with the loss of a small molecule in the process.
Komentar
Posting Komentar